Smallpox Was Not a Mild Disease
Anti-vaccine influencers are trying to rewrite the history of smallpox
Why do some people think that smallpox was a mild disease?
The usual suspects…
Smallpox Was Not a Mild Disease
In this case, you can thank Roman Bystrianyk, who is notorious for trying to bring back the fringe ideas of older anti-vaccine activists and make you think they were popular at the time.
Not that Thomas Sydenham was an anti-vaccine activists.
In fact, he lived in the pre-vaccine era!
“I assert upon my conscience that the worst case of confluent smallpox which I ever, saw, and one which proved fatal on the eleventh day, was that of a young lady who had just before been cured of rheumatism by the usual method of copious and repeated bleedings. This first showed me that bleeding was not so good a means of bringing the variolae within due limits as I thought it was. Purging, however, I have frequently observed to have this effect, and when repeated before the blood got tainted, it has brought out the subsequent variolae in the favorable form of the distinct disease.”
The Works of Thomas Sydenham, M.D
And he advocated for keeping smallpox patients cool and comfortable and to avoid bloodletting and other aggressive treatments that could be harmful and didn’t work anyway.
Also, while he never called smallpox the safest of diseases, he did note a difference in mortality rates between those who developed discrete vs. confluent type smallpox.
“I will own that sometimes smallpox will become confluent under any treatment. Then, they are always dangerous, be as careful as you may. This, however, experience enables me to assert. The patient who has kept out of bed during the day, and taken cooling drinks only from the first, has a better chance than the one who has been heated by cordials, and covered with bedclothes.”
The Works of Thomas Sydenham, M.D
It was those with discrete smallpox that likely did better with his treatments.
But know that lots of people still died when they got smallpox using Sydenham’s treatments.
In fact, the only thing that really helped get smallpox deaths under control was the introduction of the smallpox vaccine!
What about the other accounts of mild smallpox that Roman Bystrianyk writes about?
Accounts from folks like Isaac Massey who was against smallpox inoculation, believing people were born with smallpox (innate germ theory) and that any exposure set off an infection.
Who else?
John Birch — he was against the smallpox vaccine because he would lose money when folks stopped getting inoculated, his method for stopping smallpox
Montague R Leverson - the “lead quack” in the New York chapter of the American Anti-Vaccination Society
John Mason Good — although he was against unnecessary treatments for smallpox, he supported smallpox vaccines!
Henry G Hanchett - a homeopath, he wrote a book that had an “open and purely anti-vaccinationist character.,” claiming that vaccination “puts an active poison directly into the blood” and is “incapable of protecting from smallpox.”
But while there is certainly some truth that many of these early treatments like bloodletting and giving mercury based medicines could have been harmful, that doesn’t make smallpox a mild disease.
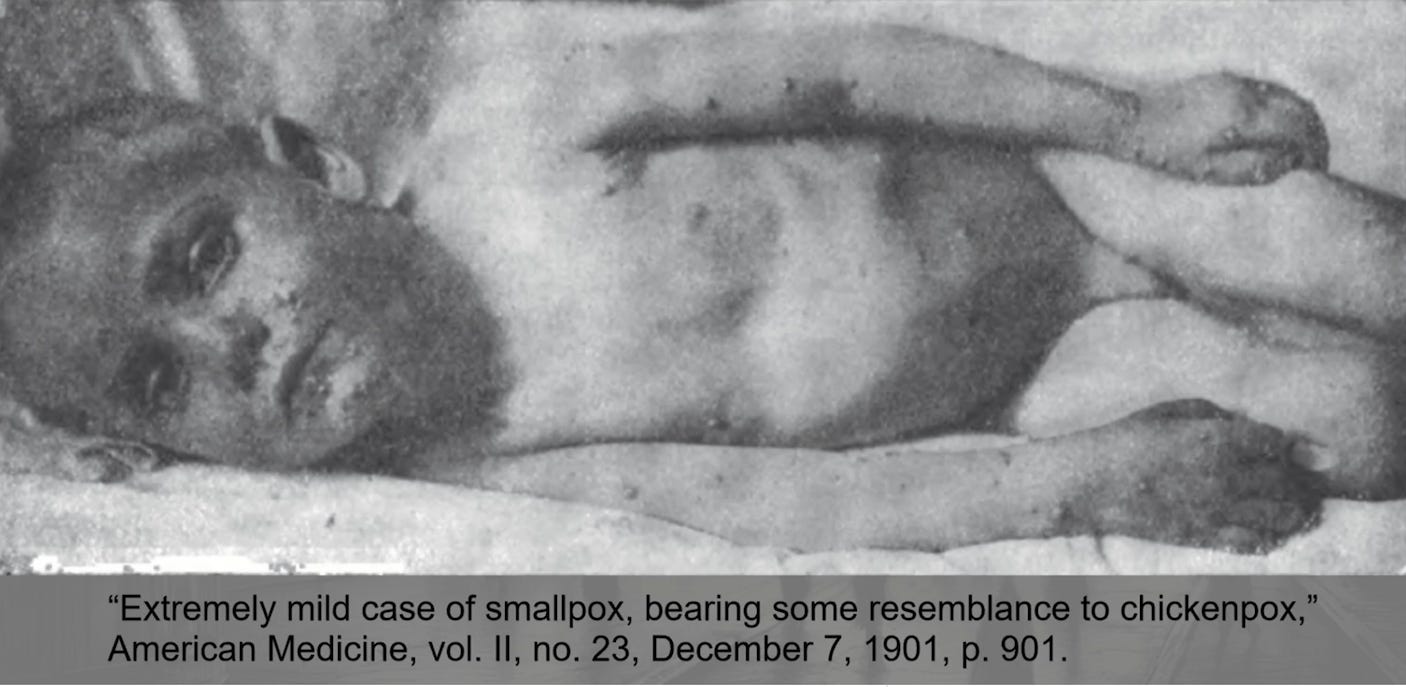
Take this pic that Roman Bystrianyk posted as proof that smallpox had become a mild disease.
The journal article was simply highlighting that mild cases could be harder to diagnose.
The article didn’t say that severe smallpox didn’t exist!
But even as we did begin to see more cases of variola minor in the United States, it is important to note that people were still dying.
And no, sanitation did not conquer smallpox.
It helped control smallpox, sure, but we still needed vaccines.
The use of “pest houses” to aggressively quarantine people with smallpox helped too, but we still needed vaccines, especially as misinformation and propaganda from the anti-vaccine movement often led to a return of smallpox.
As did a move toward ring vaccination — vaccinating all the close contacts of anyone who has smallpox.
Not surprisingly, Roman Bystrianyk goes for a hat trick in this one. He has already tried to make the case that smallpox was a mild disease and that smallpox vaccine didn’t work. And he ends talking up smallpox vaccination deaths.

None of this is really true though.
“If health officers were not sure that vaccination is safe, we would not be fools enough to vaccinate ourselves and families every two or three years.”
Charles V Chapin on The Cost of a Smallpox Epidemic
Consider the other experts that Roman Bystrianyk quotes in his video:
Dr. C Killick Millard — in addition to being against vaccines, Millard supported euthanasia and eugenics. He wrote in 1914 that smallpox will be completely banished from this country without vaccines. He was wrong.
Charles Chapin - while Bystrianyk quoted Chapin’s writings about variola minor, he left out that Chapin was a strong advocate for smallpox vaccination!
Thomas Mack — while he did say that the disappearance of smallpox was “facilitated, not impeded, by economic development,” he also stated that “prophylactic vaccination of contacts is an important containment strategy!” And his comments about universal vaccination that Bystrianyk quoted was a response to a vaccine policy to a terrorist introduction of smallpox. Not to the historical eradication of smallpox.
C Henry Kempe - while he acknowledged the dangers of smallpox vaccines for children with eczema, he developed smallpox immune globulin to help treat them, worked on a killed smallpox vaccine that would be safer for them, and said that “there is little doubt that universal vaccination has stamped out smallpox in this country!”
So, most of his experts actually supported use of the smallpox vaccine! Roman Bystrianyk just used out-of-context quotes to make you think they weren’t.

Let’s take a look at what happened in Cleveland, Ohio, for example.
They stopped using the smallpox vaccine in Cleveland in 1901.
“In early 1902 the people of Cleveland enjoyed the return of normalcy, but their sense of security was unfounded. In fact, the city had been extremely fortunate: the preceding epidemic consisted of a relatively mild, less contagious variety of smallpox (variola minor). While isolating patients and disinfecting their homes had undoubtedly helped in its containment, these measures alone could not halt a more virulent strain of smallpox (variola major).”
Smallpox: A City on the Edge of Disaster
Well, they stopped using the smallpox vaccine until a real smallpox epidemic hit their town the next year…
“The total number of cases for the year was 1,248, with 224 deaths, a death rate of 17.9 percent. This was the “genuine, old-fashioned” smallpox. Many of the cases were of the most malignant form. It was exceedingly contagious, unlike the mild form which had hitherto prevailed, and was correspondingly difficult to control.”
Ohio. Dept. of Health. Report, 1902-1903 v.17-18
And then they had to vaccinate folks again because so many people were dying.
They had to vaccinate folks with a smallpox vaccine that was known to be safe, effective, and with few risks.
“How was this sudden ending of this epidemic of smallpox brought about? By vaccination, with, of course, isolation of the patients.”
Ohio. Dept. of Health. Report, 1902-1903 v.17-18
A smallpox vaccine that eventually helped us to control and finally eradicate smallpox!
References
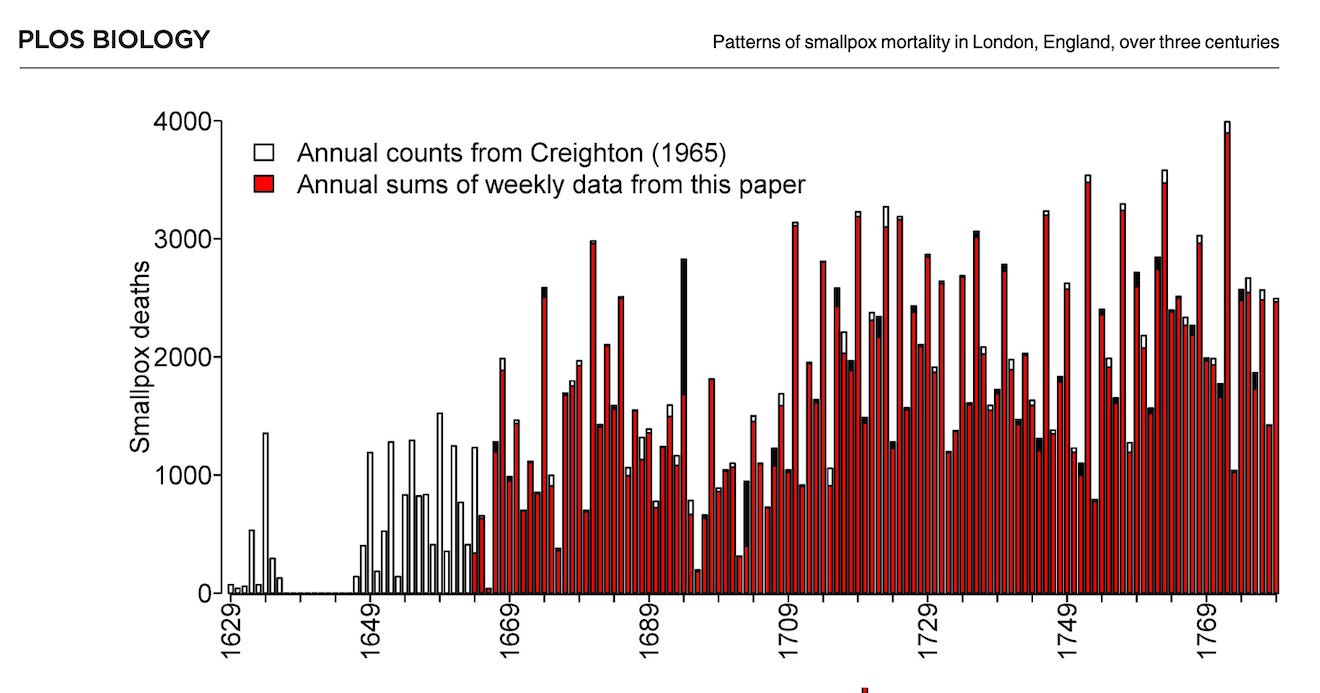
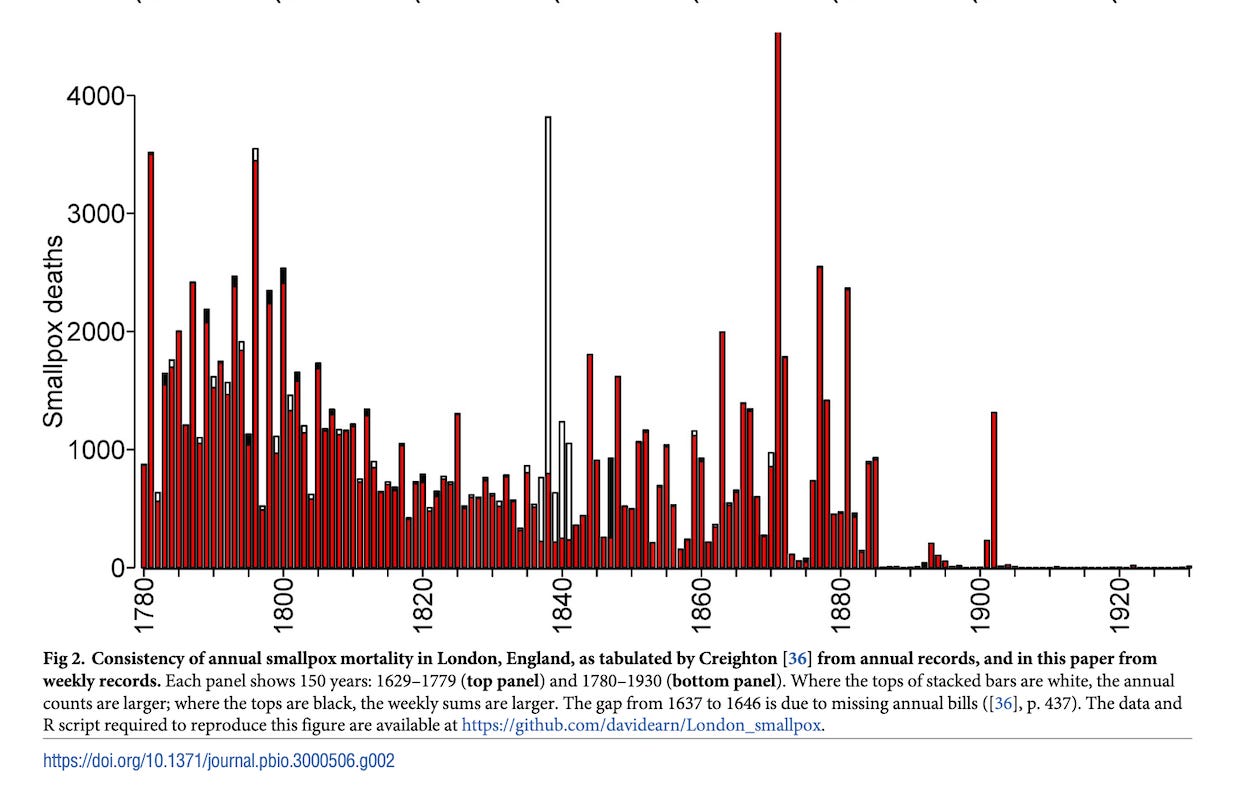
Krylova O, Earn DJD. Patterns of smallpox mortality in London, England, over three centuries. PLoS Biol. 2020 Dec 21;18(12):e3000506. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000506. PMID: 33347440; PMCID: PMC7751884.
Meyer VN. Innovations from the Levant: smallpox inoculation and perceptions of scientific medicine. Br J Hist Sci. 2022 Dec;55(4):423-444. doi: 10.1017/S0007087422000322. PMID: 36366941.
The study of medicine by Good, John Mason, 1764-1827 Publication date 1826
"The cost of a smallpox epidemic". Public Health Reports. 42 (21). U.S. Public Health Service: 1445–1446. May 27, 1927.
Mack T. A different view of smallpox and vaccination. N Engl J Med. 2003 Jan 30;348(5):460-3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsb022994. Epub 2002 Dec 19. PMID: 12496354.
C. Henry Kempe; STUDIES ON SMALLPOX AND COMPLICATIONS OF SMALLPOX VACCINATION : E. Mead Johnson Award Address. Pediatrics August 1960; 26 (2): 176–189. 10.1542/peds.26.2.176
Ohio. Dept. of Health. Report, 1902-1903 v.17-18
The Triumph of Science: The Incredible Story of Smallpox Eradication https://www.nfid.org/the-triumph-of-science-the-incredible-story-of-smallpox-eradication/
Smallpox eradication claim denies vaccine evidence https://www.aap.com.au/factcheck/smallpox-eradication-claim-denies-vaccine-evidence/